728x90

외부 서비스가 정상이 아닐 경우, 트랜잭션 처리를 어떻게 해야할까 ?
비동기 이벤트를 사용해서 두 시스템 간의 결합도를 낮춘다. ( 강결합 → 약결합 )
이벤트가 발생한다 → 상태가 변경됐다 → 해당 이벤트에 반응하여 원하는 동작을 수행하는 기능 작성
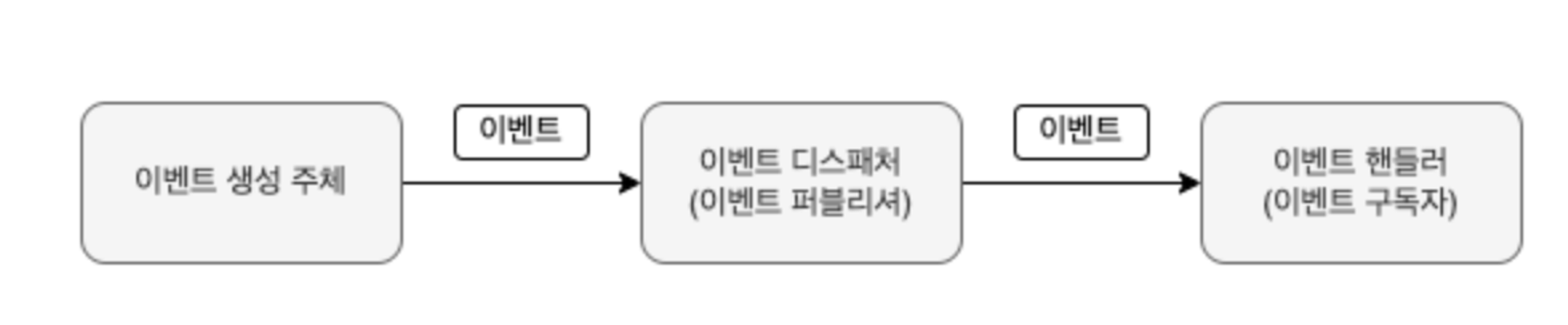
- 이벤트 클래스 : 이벤트를 표현
- 디스패처 : 스프링이 제공하는 ApplicationEventPublisher 를 이용
- Events: 이벤트를 발행, 이벤트 발행을 위해 ApplicationEventPublisher 를 사용
- 이벤트 핸들러 : 생성 주체가 발생한 이벤트를 전달받아 이벤트에 담긴 데이터를 이용해서 원하는 기능을 실행
- ex) ‘주문 취소’ 이벤트를 받는 이벤트 핸들러는 해당 주문의 주문자에게 SMS로 주문 취소 사실을 알린다.
- 이벤트 디스패처 : 이벤트 생성 주체와 이벤트 핸들러를 연결
- 이벤트의 구성
- 이벤트 종류
- 이벤트 발생 시간
- 추가 데이터 : 주문번호, 신규 배송지 정보 등 이벤트와 관련된 정보
- 이벤트의 용도
- 트리거 : 도메인의 상태가 바뀔 때 다른 후처리가 필요하면 후처리를 실행
- 서로 다른 시스템 간의 데이터 동기화 : ex) 배송지를 변경하면 외부 배송 서비스에 바뀐 배송지 정보를 전송
- 서로 다른 도메인 로직이 섞이는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
// 이벤트 클래스 : 이벤트를 처리하는데 필요한 최소한의 데이터를 포함해야 한다.
public class ShippingAddressChangedEvent {
private final Long orderId;
private final Address previousAddress;
private final Address newAddress;
//...
}
- Configuration 설정
- Events 클래스 생성 → ApplicationEventPublisher 사용
- EventHandler → 이벤트를 처리할 @EventListener 사용하여 구현
//1
@Configuration
public class EventsConfiguration {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Bean
public InitializingBean eventsInitializer() {
return () -> Events.setPublisher(applicationContext);
}
}
//2
public class Events {
private static ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
static void setPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
Events.publisher = publisher;
}
public static void raise(Object event) {
if (publisher != null) {
publisher.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
//3
public void initializePassword() {
String newPassword = generateRandomPassword();
this.password = new Password(newPassword);
Events.raise(new PasswordChangedEvent(id.getId(), newPassword));
}
@Component
public class PasswordChangedEventHandler {
@EventListener(PasswordChangedEvent.class)
public void handle(PasswordChangedEvent event) {
// 이메일 발송 코드
}
}
public class PasswordChangedEvent {
private String id;
private String newPassword;
public PasswordChangedEvent(String id, String newPassword) {
this.id = id;
this.newPassword = newPassword;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getNewPassword() {
return newPassword;
}
}
외부 서비스에 영향을 받는 경우는 어떻게 할까?
ex) 외부 환불 시스템의 요청이 오래걸려서 취소에서 딜레이가 될 경우
- 비동기 이벤트 처리 방법을 사용
- 로컬 핸들러를 비동기로 실행하기
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync // 스프링의 비동기 실행 기능 활성화
public class ShopApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ShopApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Service
public class OrderCanceledEventHandler {
private RefundService refundService;
public OrderCanceledEventHandler(RefundService refundService) {
this.refundService = refundService;
}
@Async // 추가
public void handle(OrderCanceledEvent event) {
refundService.refund(event.getOrderNumber());
}
}
2. 메시징 시스템을 이용한 비동기 구현 : RabbitMQ, Kafka 등 ..
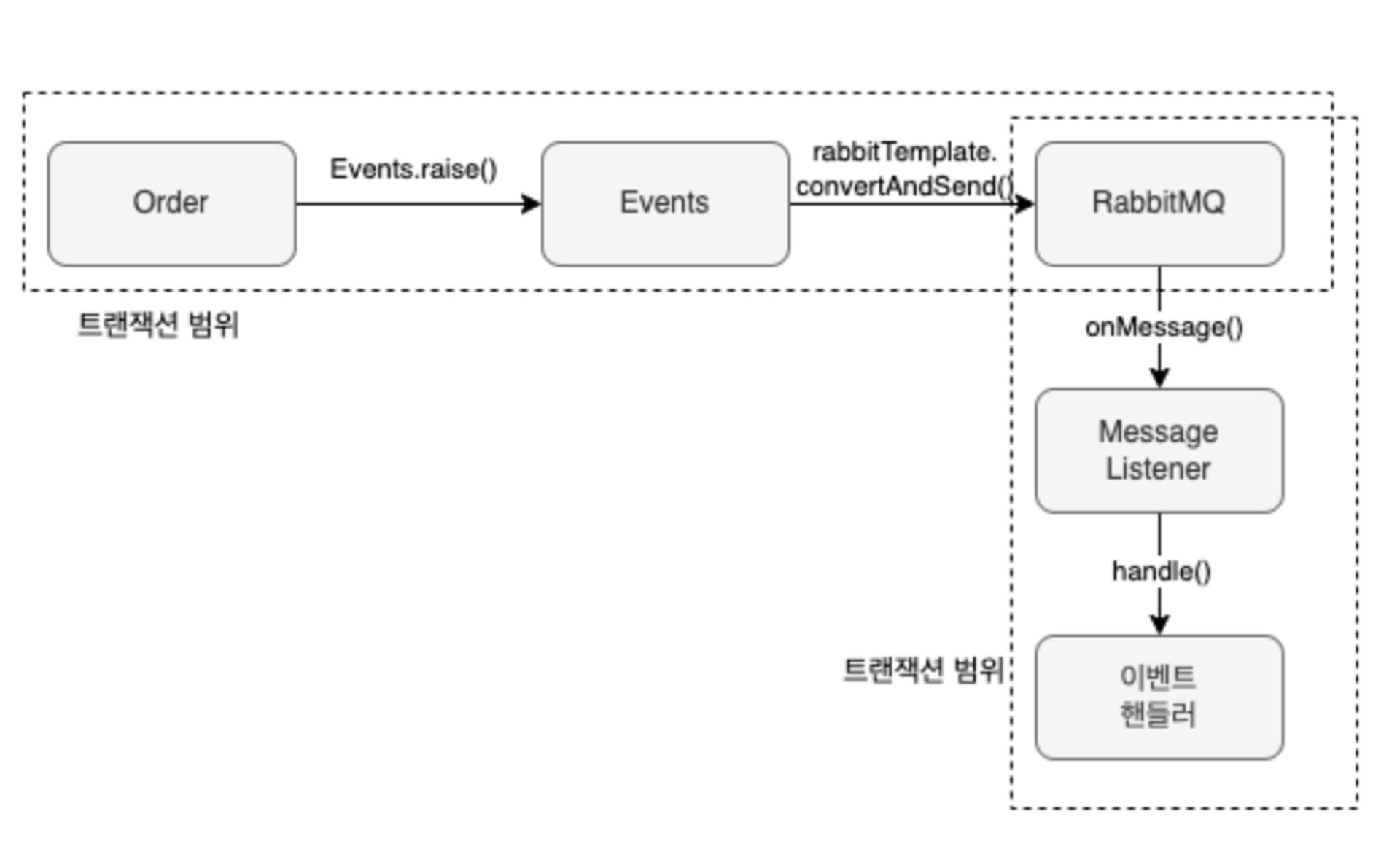
3. 이벤트 저장소를 이용한 비동기 처리
이벤트가 발생하면 핸들러는 스토리지에 이벤트를 저장한다.
포워더는 주기적으로 이벤트를 저장소에서 이벤트를 가져와 이벤트 핸들러를 실행
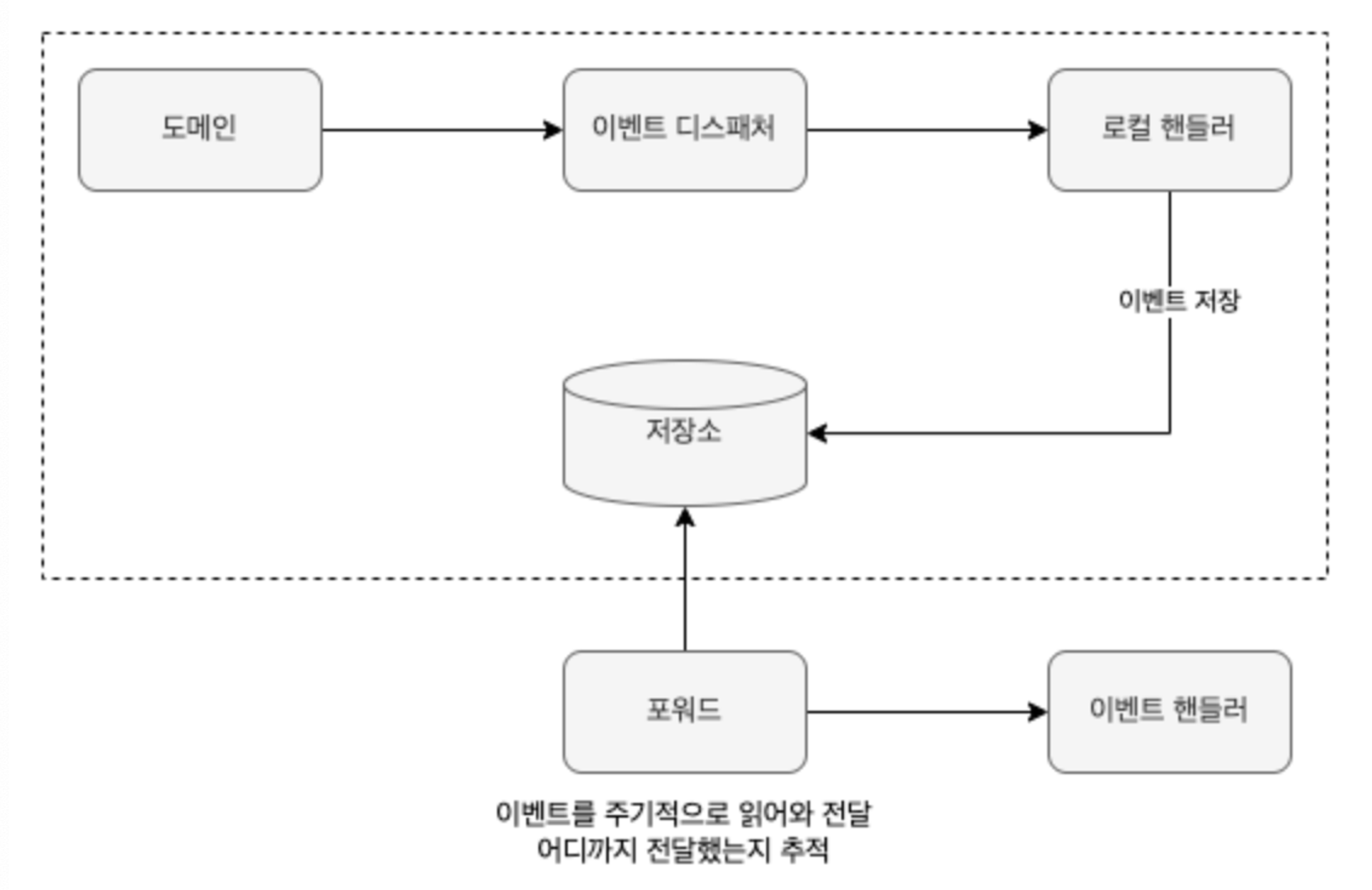
API 로 구현 : 클라이언트 API 를 이용해서 이벤트 처리에 실패하면 다시 실패한 이벤트부터 읽어와 재처리할 수 있다.
public class EventEntry {
private Long id;
private String type;
private String contentType;
private String payload;
private long timestamp;
public EventEntry(String type, String contentType, String payload) {
this.type = type;
this.contentType = contentType;
this.payload = payload;
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public EventEntry(Long id, String type, String contentType, String payload,
long timestamp) {
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
this.contentType = contentType;
this.payload = payload;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
//..
}
// 저장과 조회만 , 수정은 기능 제공X
public interface EventStore {
void save(Object event);
List<EventEntry> get(long offset, long limit);
}
// EventStore 구현
@Component
public class JdbcEventStore implements EventStore {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public JdbcEventStore(ObjectMapper objectMapper, JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public void save(Object event) {
EventEntry entry = new EventEntry(event.getClass().getName(),
"application/json", toJson(event));
jdbcTemplate.update(
"insert into evententry " +
"(type, content_type, payload, timestamp) " +
"values (?, ?, ?, ?)",
ps -> {
ps.setString(1, entry.getType());
ps.setString(2, entry.getContentType());
ps.setString(3, entry.getPayload());
ps.setTimestamp(4, new Timestamp(entry.getTimestamp()));
});
}
private String toJson(Object event) {
try {
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(event);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new PayloadConvertException(e);
}
}
@Override
public List<EventEntry> get(long offset, long limit) {
return jdbcTemplate.query(
"select * from evententry order by id asc limit ?, ?",
ps -> {
ps.setLong(1, offset);
ps.setLong(2, limit);
},
(rs, rowNum) -> {
return new EventEntry(
rs.getLong("id"),
rs.getString("type"),
rs.getString("content_type"),
rs.getString("payload"),
rs.getTimestamp("timestamp").getTime());
});
}
}
// 이벤트 저장소에 보관하기 위한 Handler
@Component
public class EventStoreHandler {
private EventStore eventStore;
public EventStoreHandler(EventStore eventStore) {
this.eventStore = eventStore;
}
@EventListener(Event.class)
public void handle(Event event) {
eventStore.save(event);
}
}
// API
@RestController
public class EventApi {
private EventStore eventStore;
public EventApi(EventStore eventStore) {
this.eventStore = eventStore;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/events", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<EventEntry> list(
@RequestParam("offset") Long offset,
@RequestParam("limit") Long limit) {
return eventStore.get(offset, limit);
}
}
/**
1. 가장 마지막에 처리한 데이터의 offset 인 lastOffset 을 구한다. 처음에는 0
2. 마지막 처리한 lastOffset 을 offset 으로 사용해서 API 실행
3. API 결과로 받은 데이터를 처리
4. offset + 데이터 처리개수를 lastOffset 으로 저장한
**/
- 포워더 구현
@Component public class EventForwarder { private static final int DEFAULT_LIMIT_SIZE = 100; private EventStore eventStore; private OffsetStore offsetStore; private EventSender eventSender; private int limitSize = DEFAULT_LIMIT_SIZE; public EventForwarder(EventStore eventStore, OffsetStore offsetStore, EventSender eventSender) { this.eventStore = eventStore; this.offsetStore = offsetStore; this.eventSender = eventSender; } @Scheduled(initialDelay = 1000L, fixedDelay = 1000L) public void getAndSend() { long nextOffset = getNextOffset(); List<EventEntry> events = eventStore.get(nextOffset, limitSize); if (!events.isEmpty()) { int processedCount = sendEvent(events); if (processedCount > 0) { saveNextOffset(nextOffset + processedCount); } } } private long getNextOffset() { return offsetStore.get(); } private int sendEvent(List<EventEntry> events) { int processedCount = 0; try { for (EventEntry entry : events) { eventSender.send(entry); processedCount++; } } catch(Exception ex) { // 로깅 처리 } return processedCount; } private void saveNextOffset(long nextOffset) { offsetStore.update(nextOffset); } } - 일정 주기로 EventStore 에서 이벤트를 읽어와 이벤트 핸들러에 전달
트랜잭션 실패를 고려해야 한다.
@TransactionalEventListener : 스프링 트랜잭션 상태에 따라 이벤트 핸들러를 실행할 수 있게 한다.
@Service
public class OrderCanceledEventHandler {
private RefundService refundService;
public OrderCanceledEventHandler(RefundService refundService) {
this.refundService = refundService;
}
@Async
@TransactionalEventListener(
classes = OrderCanceledEvent.class,
phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_COMMIT // 트랜잭션 커밋에 성공한 뒤에 핸들러 메서드를 실행
)
public void handle(OrderCanceledEvent event) {
refundService.refund(event.getOrderNumber());
}
}
728x90
'Books > 도메인 주도 개발 시작하기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter7~8. 도메인서비스 ~ 애그리거트 트랜잭션 관리 (0) | 2024.04.10 |
|---|---|
| Chapter6. 응용 서비스와 표현 영역 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| Chapter5. 스프링 데이터 JPA를 이용한 조회 기능 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| Chapter4. 리포지터리와 모델 구현 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| Chapter3. 애그리거트 (0) | 2024.04.07 |




댓글